Adjustable Back & Abdominal Support
Login For Dealer Pricing
Try Mueller’s Adjustable Back & Abdominal Support and enjoy its one handed adjustment feature that will help to flatten your stomach.
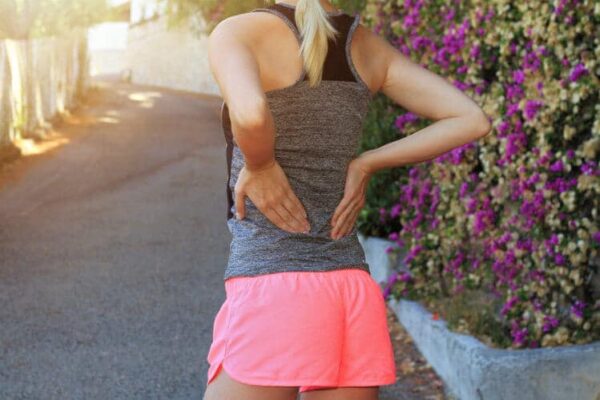

Lower back strains arise from muscle strains in the lower back or lumbar spine area below the rib cage.. They may involve overstretched muscle fibres, commonly referred to as pulled muscles. However, they can also involve partial or completely torn muscle fibres.
The main symptoms of lower back strains are swelling, inflammation and cramping in some cases. Among adults in North America, lower back strains and sprains account for a large proportion of missed work days. Together with the cost of treatment, they therefore have a significant impact on the economies of many countries.
Lower back strains are painful and unpleasant. However, , the good news is that most of them respond to conservative home based treatment. Usually, they are treatable by rest and self care with no need for surgical intervention.
However, lower back strain symptoms can sometimes closely resemble those of much more serious health problems. These can range from nerve damage to even cancer. It is therefore important to seek medical advice as soon as you experience symptoms resembling those of this injury.
Probably the main cause of lower back muscle strains is attempting to lift heavy loads. This is especially the case when this is done with an incorrect lifting technique.
Many individuals attempt to lift such a load by bending their backs to pick up the load. This then forces them to use their lower back muscles to lift the load. In many cases the lower back muscles and ligaments are not properly stretched or are not strong enough.
If so, the result can be overstretching or tearing. The result will then be a lower back muscle strain or ligament sprain.
Individuals with lower back strains will experience some or all of the following symptoms:
As mentioned above, these symptoms are also possible indicators of much more serious medical problems than a lower back muscle strain. It is therefore important to rule out these other possible causes. Do this by contacting a healthcare professional for a diagnosis and medical advice.
To diagnose the cause of the patient’s injury, doctors will ask about his or her medical history. They will usually perform a physical examination of the patient’s lower back to understand the exact location of the pain. The patient may be asked when the pain started and what he or she was doing at the time.
In rare cases, the back pain does not go away after an initial period of conservative home based self care. If so, the doctor may order an imaging scan. This may be an X Ray, MRI or CT scan.
At the end of the examination the doctor may conclude that the patient has suffered a lower back strain. If so, (s)he will usually recommend a period of home based care. This may include:
If the strain is a mild one, recovery may require as little as 2-3 days of home based treatment. However, a more serious strain (e.g. one with tearing of the muscle) may need a few weeks of recovery time.
To ensure a complete recovery, it’s important to be patient and not try to return to normal activity prematurely. Wait until there is complete freedom of movement without pain. If you return to normal activity before you are fully healed, you could re-injure yourself. You could also possibly end up with a chronic back injury.
To reduce the risk of experiencing this unpleasant injury, we suggest the following:

Login For Dealer Pricing
Try Mueller’s Adjustable Back & Abdominal Support and enjoy its one handed adjustment feature that will help to flatten your stomach.
Login For Dealer Pricing
Equipped with eight flexible steel springs that conform to your lower back for a firm yet comfortable support. Velcro closure allows for adjustment. One size fits most.

Login For Dealer Pricing
The Mueller Sports Medicine Adjustable Back Brace with Lumbar Pad can help relieve lower back pain as well as support a weak or injured back during the rehabilitation period. It features supportive springs along the spine, a removable lumbar pad and an internal molded plastic component that reduces the incidence of rolling or bunching. The brace also includes dual, outer elastic tension straps that provide a custom and comfortable fit to go with its superior level of support.
Login For Dealer Pricing
A light weight back brace designed for lower back conditions. Features include a velcro closure and a 9 inch elastic band with foam pad and steel springs and an additional 6 inch outer band for additional support.

Login For Dealer Pricing
The McDavid Back Stabilizer protects from strains and pulls with 6 steel stays strategically positioned for maximum support. Its vented elastic side panels feature hook and loop closures. The brace also includes a neoprene wrap for custom fit and comfort.
Level 3: Maximum Protection – Core support and helping to relieve non-specific back pain

Login For Dealer Pricing
The LP EmbioZ Back Support Top with Silicone features a Power System to enhance explosive and efficient use of upper torso muscles. It combines this with a moisture wicking Comfort System, General Compression and a Seamless design to create a peerless alliance of comfort, performance improvement and injury protection.
Login For Dealer Pricing
Try the Mueller Back Support with Suspenders for the blood circulation benefits of suspenders together with an effective solution to lower back pain.

Login For Dealer Pricing
It’s a Cinch, 41% reduction in low back pain
The BioSkin Baja 627 provides unrivaled lumbar support and pain relief, allowing you to return to normal activity. It has a double lacing system with the two banks of pulleys positioned on the sides of the torso. When the patient engages the cinching mechanism, the posterior panel is drawn forward, focusing the compression on the soft tissues that support the spine.
A recent study using the bilateral cinching mechanism of the Baja 627 showed an average reduction in VAS scores of 40% and a 41% improvement in Roland Morris Disability Questionnaire scores in patients with chronic low back pain.
Login For Dealer Pricing
The Mueller Green Back Brace helps protect against lower back pain, weakness and fatigue with maximum support. One size.

Login For Dealer Pricing
The Incline Board is useful for stretching the upper and lower back as well as calf muscles in order to keep the tissues in these areas warm and supple.

Login For Dealer Pricing
The McDavid Waist Trimmer helps relieve minor back pain and/or may enhance weight loss efforts via therapeutic heat. This brace cushions, compresses, and supports lower back and abdominal muscles.
Level 3: Maximum Protection – Core support and as part of a comprehensive weight loss program