Rated 5.00 out of 5
Login For Dealer Pricing
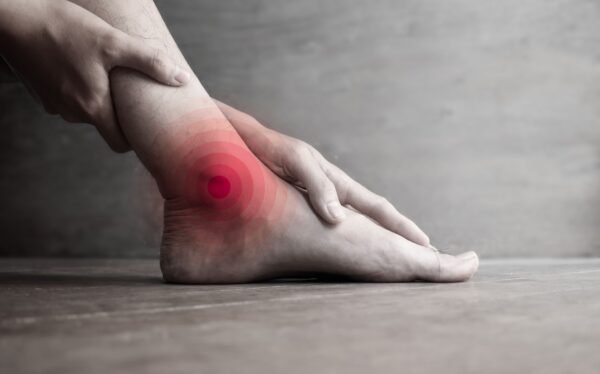
For Ankle Sprains, PTTD, and Plantar Fasciitis
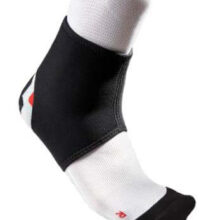
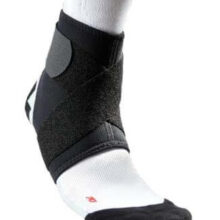
The Bio Skin TriLok has unparalleled versatility, delivering targeted unloading to medial and lateral structures.
- Positioned laterally, the FootLok™ Strap supports and protects the lateral ligaments and the peroneal tendons;
- Positioned medially, the FootLok Strap supports the plantar fascia or the posterior tibial tendon. No other brace offers such versatility;
- The included Stirrup strap provides superior lateral stability and relieves pressure on weak or injured ankle ligaments and tendons;
- The low profile and ultra comfortable TriLok is effective with almost any type of footwear or with no footwear at all;
- Made from BioSkin’s patented and highly breathable Ultima 2SL material;