Back Flex
Login For Dealer Pricing
Targeted compression for effective back pain treatment
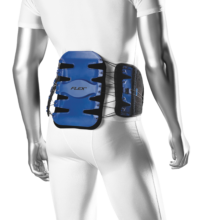
The BioSkin Back Flex is a simple and effective treatment for a variety of causes of lumbar pain. it is also helpful as a post-procedural treatment for stabilization, compression, and cold therapy. The brace includes two hot/cold gel pads that attach to the lumbar panel to enhance patient comfort and maximize pain relief.
The patent-pending design of the Back Flex provides unrivaled support and pain relief to the lower spine. The solid lumbar panel is attached to a mechanically-advantaged cinching mechanism which provides adjustable pressure to the lumbar spine. Because the cords attach the side panels to the back panel, engaging the cinching mechanism focuses the compression on the spine and provides better support than is possible with other designs.