Compression Gloves
Login For Health Care Pricing
In Stock
Mueller Sports Medicine Compression Gloves help relieve the pain associated with arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome.
Joint swelling, also known as joint inflammation or arthralgia, is a common symptom that can affect various joints in the body. It refers to the abnormal accumulation of fluid within a joint, resulting in swelling, pain, stiffness, and limited range of motion. Joint swelling can be caused by a wide range of conditions and factors.
This article aims to provide an overview of the possible causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for joint swelling.
Joint swelling can be caused by several factors, including:
Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and gout can lead to joint inflammation and swelling. These conditions are characterized by an autoimmune response, where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing inflammation.
The most common form of arthritis, osteoarthritis, is often associated with joint swelling. It occurs due to wear and tear of the joint cartilage over time, leading to joint degeneration, inflammation, and swelling.
Bacterial, viral, or fungal infections can cause joint swelling. Examples include septic arthritis, Lyme disease, and viral arthritis. Infections can lead to the accumulation of fluid in the joints, resulting in swelling and pain.
Joint swelling can occur as a result of direct trauma or injury to the joint, such as sprains, strains, fractures, or dislocations. The body’s natural response to injury includes inflammation and swelling.
Bursae are fluid-filled sacs that cushion and reduce friction between bones, tendons, and muscles around the joints. When bursae become inflamed, a condition called bursitis, joint swelling can occur.
Inflammation of the tendons, known as tendonitis, can cause joint swelling near the affected tendon. This condition often results from overuse, repetitive motions, or injury.
To diagnose the cause of joint swelling, healthcare professionals may rely on the following procedures:
A detailed discussion of symptoms, medical history, and recent activities is essential. The healthcare provider will examine the affected joint(s) for swelling, redness, warmth, tenderness, and range of motion.
X-rays, MRI scans, or ultrasound may be used to visualize the joint structures, identify any damage, assess the extent of inflammation, or detect signs of underlying conditions.
Laboratory tests, such as complete blood count (CBC), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP), and rheumatoid factor (RF), may be performed to evaluate inflammation levels and determine if an autoimmune condition is present.
In some cases, a procedure called joint aspiration or arthrocentesis may be conducted. This involves removing fluid from the affected joint with a needle for further analysis, such as to rule out infection or evaluate the characteristics of the fluid.
The treatment approach for joint swelling depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Treatment options may include:
Resting the affected joint and avoiding activities that worsen the swelling is crucial for allowing the joint to heal. Immobilization, such as using a splint or brace, may be recommended to provide support and limit movement.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), corticosteroids, or disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, alleviate pain and manage underlying conditions contributing to joint swelling.
A physical therapist can design a customized rehabilitation program to improve joint mobility, strength, and stability. Therapeutic exercises, stretches, and modalities can help reduce swelling, improve joint function, and prevent future episodes.
Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation (RICE) can be beneficial in managing joint swelling caused by acute injuries or overuse. Applying ice packs, compressive bandages, and elevating the affected joint can help reduce swelling and promote healing.
In certain cases, healthcare providers may recommend corticosteroid injections into the affected joint to provide localized anti-inflammatory effects and relieve swelling and pain.
In severe cases where joint swelling is caused by significant damage or structural abnormalities, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as arthroscopy, joint replacement, or synovectomy may be considered.
While not all causes of joint swelling can be prevented, some preventive measures can help reduce the risk of developing joint-related problems:
Excess weight can put additional stress on joints, increasing the risk of joint damage and inflammation. Maintaining a healthy weight can help prevent excessive joint strain.
Engaging in regular low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help strengthen muscles, improve joint flexibility, and reduce the risk of joint swelling and injuries.
Using appropriate protective gear, such as supportive braces or equipment, during sports or activities that involve repetitive joint movements can help prevent joint swelling and injuries.
Maintaining good posture and using ergonomic techniques in daily activities can reduce joint stress and minimize the risk of joint-related issues.
Proper hydration is important for joint health. Drinking an adequate amount of water can help keep joints lubricated and reduce the risk of inflammation.
Joint swelling can be a distressing symptom that impacts an individual’s quality of life and functionality. Identifying the underlying cause of joint swelling through proper diagnosis is essential for implementing an appropriate treatment plan. Seeking medical advice from healthcare professionals, such as rheumatologists, orthopedic specialists, or physical therapists, is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment approach.
By addressing joint swelling promptly and following recommended treatment strategies, individuals can alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, improve joint function, and enhance their overall well-being.

Login For Health Care Pricing
In Stock
Mueller Sports Medicine Compression Gloves help relieve the pain associated with arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome.

Login For Health Care Pricing
In Stock
The econo-wrap latex free elastic bandage provides a comfortable, safe, and hypoallergenic alternative for individuals with latex allergies, without compromising on quality or performance. It delivers firm, customizable support, making it perfect for managing injuries, swelling, or offering preventative support during physical activity.
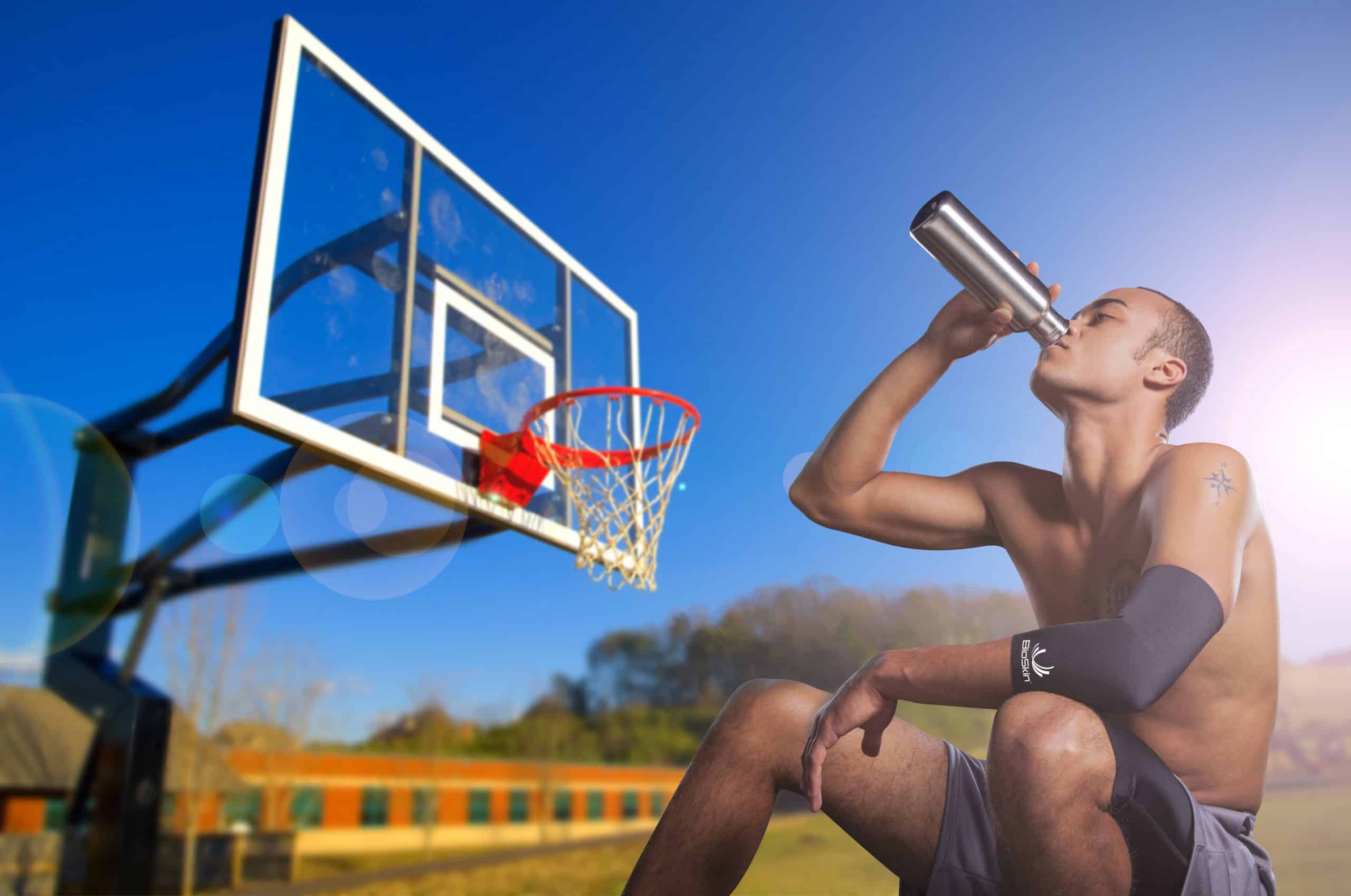


Login For Health Care Pricing
In Stock
The Bio Skin Standard Elbow Skin provides full elbow coverage and optimal compression for treatment of elbow pain caused from contusion, bursitis, and joint swelling. Constructed from Bio Skin’s patented thin, breathable, Ultima™ material, which keeps you cool and dry and quickly wicks moisture away from the skin