Heel Cups
Login For Health Care Pricing
Typically Ships in 1-2 weeks
Mueller Heel Cups reduce heel strike pain and ease the discomfort of shin splints, heel spurs and related conditions. One pair.

Heel pain is a common complaint that can significantly impact daily activities and mobility. The heel is a weight-bearing structure, and pain in this area can be debilitating and affect one’s quality of life. Understanding the potential causes and having an accurate diagnosis as well as appropriate treatment options for heel pain are essential for effective management.
This article aims to explore the possible causes of heel pain, discuss the diagnostic process, and provide insights into treatment approaches.
Heel pain can arise from various factors, including:
This is the most common cause of heel pain. Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that supports the arch of the foot, becomes inflamed or strained. It often results from repetitive stress or excessive stretching of the fascia.
Achilles tendinitis refers to inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. It is commonly seen in runners and athletes involved in activities that require repetitive jumping or pushing off the foot.
Heel spurs are bony protrusions that can develop on the underside of the heel bone. They are often associated with plantar fasciitis but can also occur independently. Heel spurs themselves may not cause pain, but they can contribute to the overall discomfort in the heel area.
This condition typically affects children and adolescents during periods of rapid growth. It involves inflammation of the growth plate in the heel bone and is commonly seen in active children involved in sports activities.
Bursitis occurs when the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that provide cushioning, become inflamed. In the heel, bursitis can develop in the retrocalcaneal bursa, located at the back of the heel bone.
Stress fractures are small cracks in the bone caused by repetitive stress or overuse. They can occur in the heel bone (calcaneus) and are often seen in athletes engaged in high-impact activities.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial in determining the underlying cause of heel pain. The diagnostic process may include:
The healthcare provider will discuss the individual’s medical history, including the details of the pain, its onset, duration, and aggravating factors. A thorough physical examination of the foot and ankle is conducted, assessing for tenderness, swelling, and range of motion.
X-rays may be ordered to assess the bony structures and rule out fractures, while ultrasound or MRI scans can provide detailed images of soft tissues, such as tendons and ligaments.
In some cases, a biomechanical evaluation may be performed to assess foot structure, alignment, and gait patterns. This can help identify any biomechanical abnormalities that may contribute to heel pain.
Treatment options for heel pain depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common approaches include:
Resting the affected foot, reducing activities that worsen the pain, and avoiding high-impact exercises can promote healing and alleviate symptoms.
Applying ice packs or cold compresses to the heel can help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Heat therapy, such as warm foot baths or heating pads, may also provide relief for certain conditions.
Stretching exercises for the calf muscles, Achilles tendon, and plantar fascia can improve flexibility and alleviate symptoms. Strengthening exercises for the foot and ankle muscles can help provide support and stability.
Wearing orthotic devices, such as shoe inserts or custom-made orthotics, can provide support, cushioning, and promote proper foot alignment, thereby reducing stress on the heel.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or pain-relieving medications may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
A physical therapist can develop a customized rehabilitation program that includes stretching, strengthening, and proprioception exercises to address the underlying causes of heel pain and promote healing.
Wearing supportive and well-fitted footwear with adequate arch support can help reduce strain on the heel and provide comfort during activities.
In cases of severe pain or inflammation, corticosteroid injections may be administered by a healthcare professional to provide temporary relief.
ESWT is a non-invasive procedure that uses shockwaves to stimulate healing and reduce pain in certain cases of chronic heel pain.
Heel pain can significantly impact an individual’s daily activities and quality of life. Understanding the possible causes, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment options are crucial for effective management. Seeking professional medical advice from a sports medicine specialist, orthopedic surgeon, or podiatrist is recommended for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
With proper diagnosis and targeted interventions, individuals with heel pain can alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and regain their mobility and comfort.

Login For Health Care Pricing
Typically Ships in 1-2 weeks
Mueller Heel Cups reduce heel strike pain and ease the discomfort of shin splints, heel spurs and related conditions. One pair.

Login For Health Care Pricing
Out of Stock
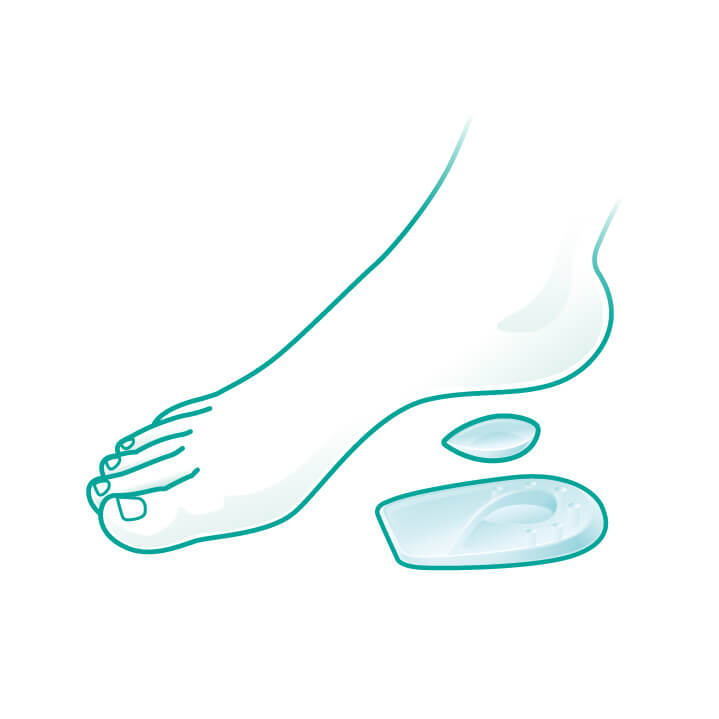
Heel Cushions with Removable Pads from Oppo that reduce shocks to the joints and vertebral column while walking or running.

Login For Health Care Pricing
Out of Stock
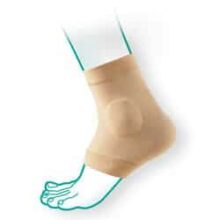
The Oppo Malleolar Sleeve will protect the medial and lateral sides of the malleolus (the bony bumps on each side of the ankle) from shock and vibration. One Size.

Login For Health Care Pricing
In Stock
Mueller Pro Heel Cups are designed to help athletes in high impact sports by reducing the impact of shocks to the heels that may cause foot and knee injuries.


Login For Health Care Pricing
Out of Stock
Oppo Step Easy Full Length Insoles ease foot pain from heel strikes and also provide arch support.

Login For Health Care Pricing
Out of Stock
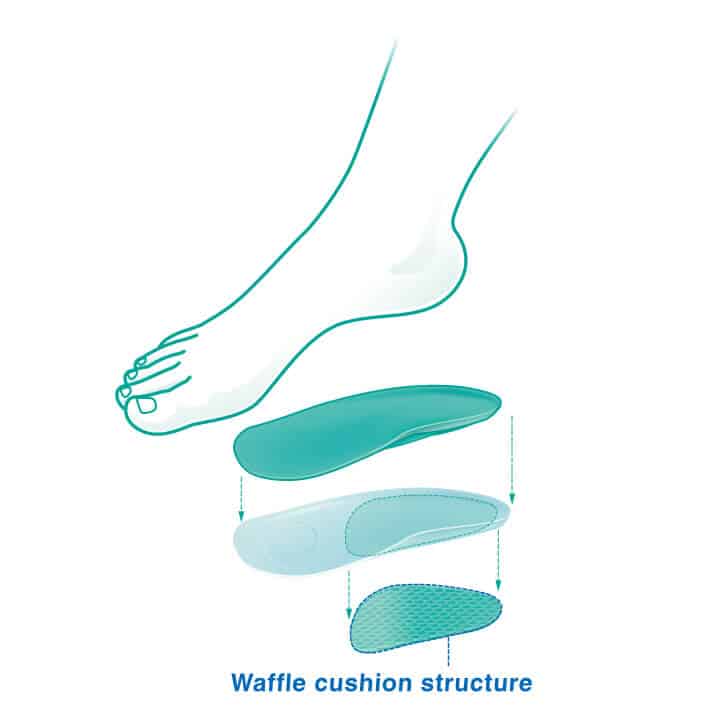
Waffle Comfort Arch Supports from Oppo absorb shocks to the foot and ease heel and plantar fasciitis pain.


Login For Health Care Pricing
Out of Stock
Waffle Support Gel Insoles from Oppo provide cushioning and protection to both the heel and metatarsal areas (just behind the toes) and reduce both heel pain and metatarsalgia.