4 Differences Between Athletic Therapy & Physiotherapy
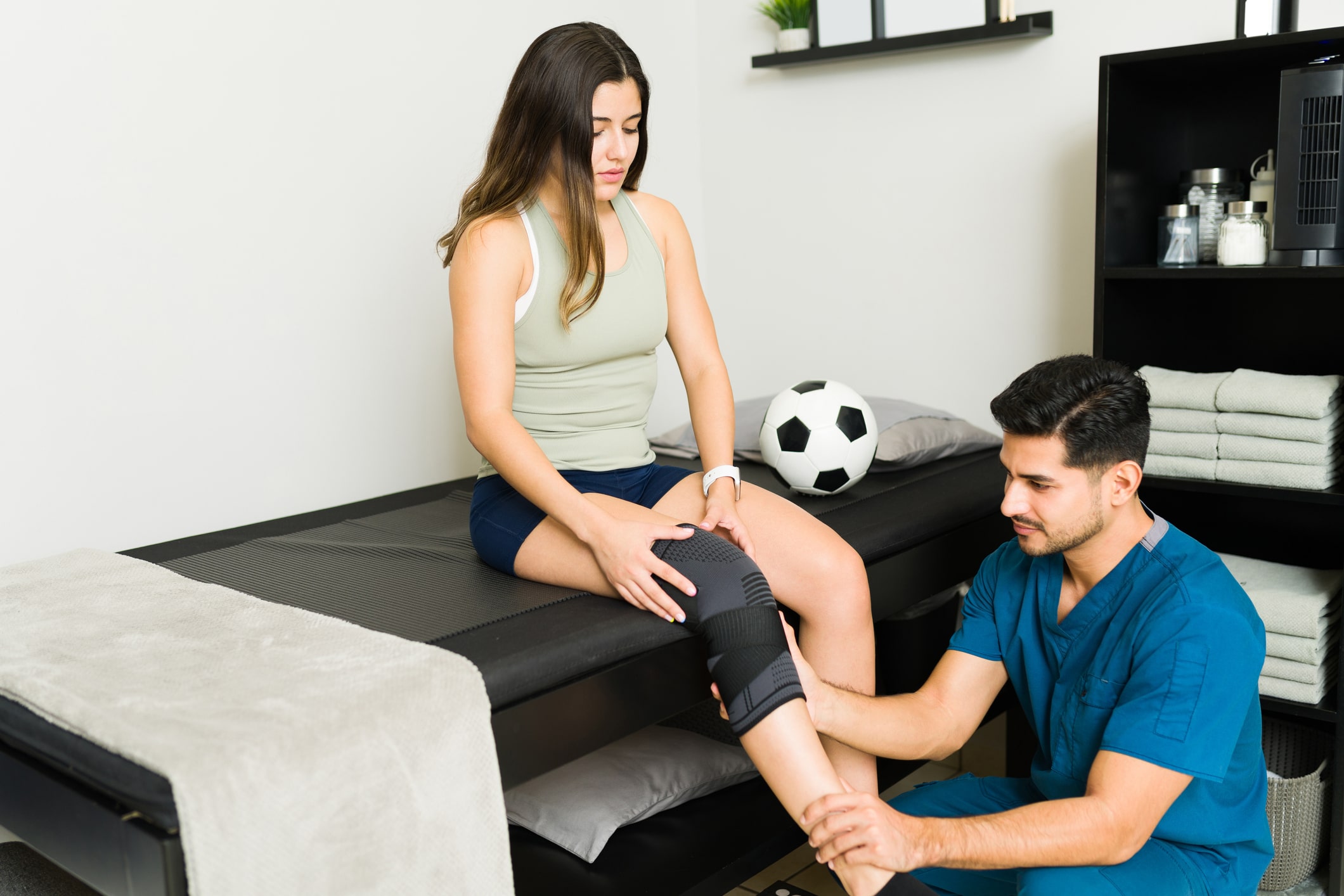
The fields of athletic therapy and physiotherapy have plenty of things in common. Both physiotherapists and athletic therapists are trained in the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries. They focus on treating and rehabilitating injured muscles and joints and assisting their patients to return to their normal activities. They both employ hands on treatment techniques including manual therapy.
However, they are at the same time different disciplines. In this article we explain 4 of the key differences between these closely related fields. We hope that this will help those interested in one or both fields make decisions that lead to a satisfying career.
Differences Between Athletic Therapy & Physiotherapy
We will now lay out 4 of the key differences between these professions.
Scope of Practice
Probably the main difference between the two fields is in the scope of practice. Athletic therapists tend to focus primarily on sports injuries such as shin splints and hamstring strains. They have usually had extensive exposure to sporting environments. This gives them a particular expertise in treating injuries sustained from these activities.
Physical therapists will also treat these injuries. However, in general, they have a broader focus in terms of the types of injuries and disorders treated. Physical therapists can for example treat illnesses and diseases that have neurological and respiratory components. So patients with multiple conditions, both related and unrelated to sports activities, are probably more treatable by a physiotherapist.
Types of Activities
Physiotherapists’ treatment plans aim to rehabilitate their patients and prepare them for a return to “regular” activities. These may be activities related to their occupation or even to their recreational interests such as gardening. They may even include the weekend pursuit of a sporting activity. But in most cases, they will not include the long hours of intense physical training required of a serious athlete.
Athletic therapists, however, are more focused on helping the patient return to a physical condition for a specific sporting activity. Their rehabilitation techniques are especially focused on the treatment of serious athletes. These individuals face more rigorous demands on their bodies than the rest of the population.
Route To Qualification
Athletic therapists require a bachelor’s degree from a qualified university and several hundred hours of practical internship. They must also pass written and practical board examinations in order to obtain a practising license.
Like athletic therapists, physical therapists must also complete hundreds of practical hours before qualification. They too have to complete written and practical exams to obtain a license.
However, the difference lies in the amount of formal education required. Physiotherapy requires not just a bachelor’s but also a master’s degree from a recognized university. The master’s degree usually covers subjects like orthopedics, cardio-respiratory rehabilitation, pediatrics and neurological disorders, to name a few.
Areas Of Specialized Training
Both athletic therapists and physical therapists share a number of areas in which specialized training may be pursued. These include Kinesio Taping and Personal Training / Strength, to take a few examples.
However, there are a number of areas of specialization that are unique to physical therapy. These can include, for example, orthopedic manipulation, dry needling and women’s health.
Conclusion
In this article, we have tried to highlight the main differences between physiotherapy and athletic therapy. A certain amount of generalization is unavoidable. However, the information presented should help the reader to understand the key distinctions between these closely related but distinct professions.