Support de poignet réglable
Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
Le support de poignet réglable Mueller Sport Care traite les poignets faibles, blessés ou instables sans réduire l'amplitude des mouvements.
Wrist pain can be a debilitating condition that hinders daily activities and affects overall quality of life. The wrist is a complex joint composed of bones, ligaments, tendons, and nerves, and various factors can contribute to the development of wrist pain.
In this article, we will explore the common causes, methods of diagnosis, and treatment options for wrist pain.
Wrist sprains occur when the ligaments that support the joint are stretched or torn, often due to a fall or sudden impact. Strains, on the other hand, involve the stretching or tearing of muscles and tendons in the wrist.
This condition occurs when the median nerve, which runs through a narrow passage in the wrist called the carpal tunnel, becomes compressed or irritated. CTS is often associated with repetitive hand and wrist movements, such as typing or using vibrating tools.
Tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendons in the wrist. It can result from overuse, repetitive motions, or injury. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis, a specific type of tendinitis, affects the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist.
Various forms of wrist arthritis, such as osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, can affect the wrist joint, leading to pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Wrist fractures or dislocations can occur due to falls, sports injuries, or traumatic accidents. These injuries often cause immediate pain and require medical attention.
When diagnosing wrist pain, healthcare professionals employ various methods to determine the underlying cause. These may include:
The doctor will review the patient’s medical history and inquire about the nature and duration of the pain. A physical examination will be performed to assess the range of motion, swelling, tenderness, and any signs of injury.
X-rays can help identify fractures, dislocations, or signs of arthritis. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or ultrasound may be ordered to obtain more detailed images of the soft tissues, such as tendons or ligaments.
In cases suspected of nerve-related conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome, nerve conduction studies may be conducted to evaluate nerve function and identify potential compression sites.
The treatment approach for wrist pain depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Some common treatment options include:
Minor injuries or overuse injuries often benefit from rest and temporary immobilization through splints or braces. This allows the wrist to heal and reduces strain on the affected area.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation associated with wrist injuries or arthritis. In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be prescribed to alleviate severe inflammation and pain.
A customized physical therapy program can help strengthen the wrist, improve flexibility, and promote healing. Therapists may incorporate exercises, manual techniques, and modalities such as ultrasound or electrical stimulation.
In cases of conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or tendinitis, modifying occupational or daily activities to reduce repetitive motions or adopting ergonomic techniques can alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage.
In more severe cases or when conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures can range from arthroscopy (minimally invasive surgery) to repair ligaments or remove damaged tissue, to joint replacement or fusion in cases of severe arthritis.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan for wrist pain. Early intervention and proper management can significantly improve symptoms, promote healing, and prevent long-term complications.
In conclusion, wrist pain can arise from various causes, including sprains, strains, carpal tunnel syndrome, tendinitis, arthritis, fractures, or dislocations. Diagnosis often involves a medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests.
Treatment options range from conservative measures like rest, medication, and physical therapy to surgical interventions for severe cases. Prompt and proper management of wrist pain is crucial to relieve symptoms, restore function, and enhance the overall quality of life.

Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
Le support de poignet réglable Mueller Sport Care traite les poignets faibles, blessés ou instables sans réduire l'amplitude des mouvements.


Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
L'orthèse de poignet Mueller Sports Medicine Hg80 est dotée de ressorts en acier pour stabiliser votre poignet. Idéale pour la lutte, le volley-ball et le squash. S'adapte aux deux poignets.
Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
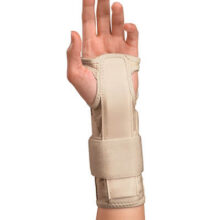
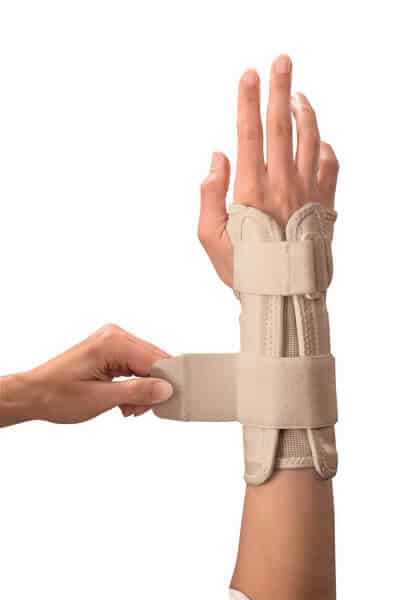
The Mueller Reversible Wrist Stabilizer brace features an extra long (6.5″) removable metal spoon stay to treat carpal tunnel and two padded side splints for lateral support. Made from breathable fabric for extra wearing comfort.

Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
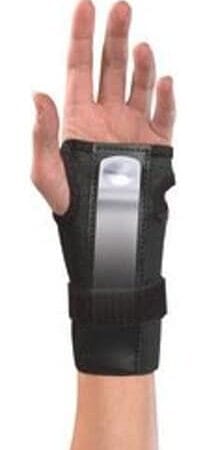
L'orthèse de poignet avec attelle de Mueller utilise une attelle amovible et rembourrée pour stabiliser le poignet dans le cadre du traitement du canal carpien. Des languettes réglables et un tissu respirant augmentent le confort de l'orthèse.

Login For Health Care Pricing
En stock
Le McDavid Wrist Sleeve / Adjustable/Elastic fournit une légère compression pour le soutien des tissus mous avec moins de rétention de chaleur.
Niveau 2 : Protection avancée - Soutien, soulagement de la douleur et promotion de la guérison

Login For Health Care Pricing
Typically Ships in 3-5 Business Days
Le McDavid Wrist Wrap / Adjustable est extensible dans les 4 sens et offre une thérapie thermique et de compression. Il est doté de fermetures à boucles et à crochets pour un ajustement et un confort personnalisés.
Niveau 1 : Protection primaire - Soutien du poignet, favorisant la cicatrisation et le soulagement de la douleur